(Geometry: n-sided regular polygon) In an n-sided regular polygon all sides have the same length and all angles have the same degree (i.e., the polygon is both equilateral and equiangular). Design a class named RegularPolygon that contains:
- A private int data field named n that defines the number of sides in the polygon with default values 3.
- A private double data field named side that stores the length of the side with default value 1.
- A private double data field named x that defines the x-coordinate of the polygon’s center with default value 0(zero).
- A private double data field named y that defines the y-coordinate of the polygon’s center with default value 0(zero).
- A no-arg constructor that creates a regular polygon with default values.
- A constructor that creates a regular polygon with the specified number of sides and length of side, centered at (0, 0).
- A constructor that creates a regular polygon with the specified number of sides, length of side, and x-and y-coordinates.
- The accessor and mutator methods for all data fields.
- The method getPerimeter() that returns the perimeter of the polygon.
- The method getArea() that returns the area of the polygon. The formula for computing the area of a regular polygon is
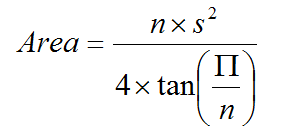
- The toString() method that returns a string representation of a RegularPolygon object
Write a test program, TestRegularPolygon, that creates three RegularPolygon objects, created using the no-arg constructor, using RegularPolygon(6, 4), and using RegularPolygon(10, 4, 5.6, 7.8). For each object, display its area and perimeter.
RegularPolygon.java
/**
* Regular Polygon.
*/
public class RegularPolygon {
// Declare and initialize default values.
private int n = 3;
private double side = 1.0;
private double x = 0.0;
private double y = 0.0;
// Create constructor with default values.
public RegularPolygon(){
}
// Create constructor with new n and side values.
public RegularPolygon(int n, double side){
this.n = n;
this.side = side;
this.x = 0;
this.y = 0;
}
// Create constructor with new n, side, x, and y values.
public RegularPolygon(int n, double side, double x, double y){
this.n = n;
this.side = side;
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
// get n method
public int getN(){
return this.n;
}
// set n method.
public void setN(int n){
this.n = n;
}
// get side method.
public double getSide(){
return this.side;
}
// set side method.
public void setSide(double side){
this.side = side;
}
// get x-coordinate method.
public double getX(){
return this.x;
}
// set x-coordinate method.
public void setX(double x){
this.x = x;
}
// get y-coordinate method.
public double getY(){
return this.y;
}
// set y-coordinate method.
public void setY(double y){
this.y = y;
}
// Calculate Perimeter.
public double getPerimeter(){
return this.n * this.side;
}
// Calculate Area.
public double getArea(){
return (this.n * Math.pow(this.side,2)) / (4 * Math.tan(Math.PI/this.n));
}
// Pepresentation method of RegularPolygon object.
public String toString(){
String result;
if(this.n >= 3 && this.side > 0){
result = "The Regular Polygon n: " + this.n + ", side: "+ this.side + ", Area: " + this.getArea() + ", Perimeter: " + this.getPerimeter();
}else if(this.n >= 3 && this.side <= 0){
result = "The side length must be greater than zero.";
}else if(this.n < 3 && this.side > 0){
result = "The number of edges must be greater than three.";
}else{
result = "The side length must be greater than zero and the number of edges must be greater than three.";
}
return result;
}
} // End of RegularPolygon class.
TestRegularPolygon.java
/**
* Regular Polygon.
*/
public class TestRegularPolygon{
/** main Method */
public static void main(String [] args){
// Create RegularPolygon object.
RegularPolygon reg0 = new RegularPolygon();
RegularPolygon reg1 = new RegularPolygon(6,4);
RegularPolygon reg2 = new RegularPolygon(10,4,5.6,7.8);
// Print RegularPolygon object values.
System.out.println(reg0);
System.out.println(reg1);
System.out.println(reg2);
} // End of main method
} // End of TestRectangle class.
Yorum Yok:
Yorum Yap:
Yorum yapabilmek için giriş yapmalısınız.